SCRUBBER
Scrubbers remove unwanted gases and particulate matter from industrial smokestacks before they enter the atmosphere. The two main types of scrubbers wet scrubbers and dry scrubbers can reduce up to 90 percent of emissions that contribute to smog and acid rain.
WET SCRUBBER:
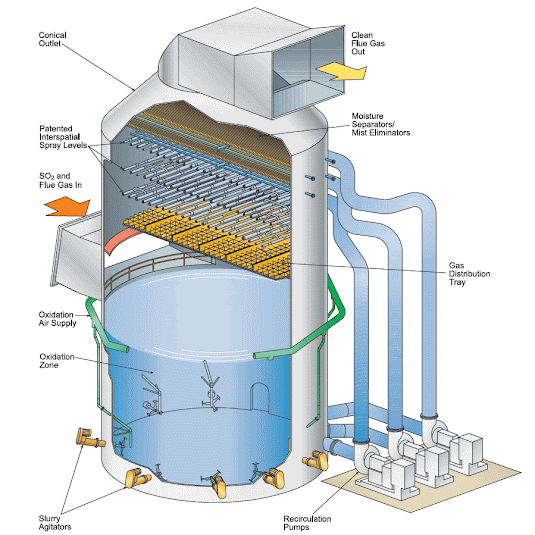
Wet scrubbers are utilized when a gas stream becomes contaminated by particulate or a gas, or a combination of both. Some gas pollutants could be ammonia, chlorine, or sulfur compounds. In the wet scrubber, these gasses will be dissolved or absorbed into the scrubbing liquid. The liquid many times is water, but can vary depending on the pollutant. In Industrial exhaust systems these harmful gasses or particulates must be removed to ensure optimal performance and compliance. Particulate matter is microscopic or liquid matter that finds its way into the gas stream. When the liquid comes into contact with the dust particulate, the heavier and coarser particles are washed out and carried down to make contact with the mist eliminator pads.
DRY SCRUBBER:
A dry scrubber or dry scrubber system is one type of scrubber that is used to remove harmful materials from industrial exhaust gases before they are released into the environment. Dry scrubbers are the type most commonly used in plants today, and they utilize a collection of dry substances to remove acidic gases that contribute to acid rain.
Dry scrubbers work similarly to other scrubbers. The system sprays a collection of dry reagents into an exhaust stream. These chemicals can react differently depending on which material they are specifically targeting for removal. Some of these materials neutralize harmful pollutants in the stream through a chemical reaction, while others cause a material to react and turn into a different substance. That substance then falls out of the gas stream or is caught in a particle screen.
VENTURI WET SCRUBBER:
Venturi scrubbers are perfect for collecting fine particulate and liquid mists. Using the differential between high velocity gases and free-flowing water to create contaminant-entrapping droplets, these scrubbers can suspend and contain a multitude of pollutants in your system. By maintaining high gas velocities and turbulence in the throat of the design you can achieve high collection efficiencies, ranging from 90% to 99% for particles with a diameter larger than 1 µm and greater than 80% for submicron particles.
PACKED TOWER WET SCRUBBER:
Packed tower scrubbers, also called packed bed or packed column scrubbers, are best for getting rid of gas phase emissions like sulfur dioxide or other odors and acids. By chemical scrubbing contaminants from your gas streams, these types of scrubbers, when designed correctly, can remove toxic or otherwise harmful emissions from gas streams and exhaust clean air into the environment. Internal packing within the scrubber provides a large wetted surface area that forces a close-contact interaction between the scrubbing liquid and the contaminated airflow. The scrubbing liquid then either absorbs or reacts with the contaminants, effectively removing them from the air. The typical collection efficiency range is from 90% to 99%, with that efficiency becoming greater than 99% for select pollutant systems. Packed tower scrubbers are less effective when dealing with particulate matter control, as high concentrations of dust can easily clog the bed of the tower.
Advantages
- Can handle flammable and explosive dusts with little risk
- Provides gas absorption and dust collection in a single unit
- Provides cooling of hot gases
- Compact; can often be retrofitted into existing collection systems
- Corrosive gases and dusts can be neutralized
Disadvantages
- High potential for corrosion problems
- Collected particulate may be contaminated and unrecyclable
- Protection against freezing required. Certain streams may require reheating to avoid visible plume
- Disposal of waste sludge can be very expensive
- Requires makeup water to replace purged liquid and disposed sludge
WORKING OF SCRUBBER:
<< READ OTHER INTERESTING POST >>
PIPING SUPPORTS
EXPANSION LOOP CALCULATION
DISTILLATION COLUMN PIPING
PIPE RACK PIPING
TYPES OF GASKET
OIL & GAS PROCESS
PDMS & E3D COMMANDS
TYPES OF STORAGE TANK  | |
READ POST >> |
|
















































Follow Us
“Science is about knowing, engineering is about doing.”