Types of Pipe Support
Rigid Support
Rigid supports are used to restrict pipe movement in certain direction(s) without any or limited flexibility in that direction. Main function of a rigid support can be:
Anchor or 3 Dimensional Stop
In this type of support arrangement, pipe is fixed with reference to the supporting structures. Movement in any direction is not allowed. This can be achieved by welding or bolting the support with supporting structure.
Rest or Sliding Support
In this type of support arrangement, pipe is fixed with reference to vertical downward direction. Movement in downward vertical direction, mainly due to the weight of pipe and containing fluid, is not allowed. This support is sometimes also referred as sliding support.
Guide
In this type of support arrangement, pipe is fixed with reference of directions other then the direction in which weight of pipe and containing fluid is acting. Limited flexibility can be provided with the provision of guide gap (gap between pipe outer surface and guide plate inner surface).
Both Rest & Guide
In this type of support arrangement, pipe is fixed with reference to vertical downward direction along-with any or all the guide directions.

Spring Support
Spring supports are used to support a load and allow simultaneous movement. Spring supports use helical coil compression springs (to accommodate loads and associated pipe movements due to thermal expansions). The critical component in both the type of supports are Helical Coil Compression springs. They are broadly classified into,
Variables Effort support
Variable effort supports also known as variable hangers or variables are used to support pipe lines subjected to moderate (approximately up to 50mm) vertical thermal movements. Variable effort supports are used to support the weight of pipe work or equipment along with weight of fluids while allowing certain quantum of movement with respect to the structure supporting it. Hot load is the working load of the support in the “Hot” condition i.e. when the pipe has traveled from the cold condition to the hot or working condition. Load Variation (LV) or Percentage variation =[(Hot Load-Cold Load) x 100]/Hot Load or [(Travel x Spring Rate) x 100]/Hot Load. Normally MSS-SP58 specifies max Load Variation ( popularly called LV) as 25%.
Constant effort support
Constant effort supports are used to support pipe lines subjected to large vertical movements typically 150 mm or 250 mm. For pipes which are critical to the performance of the system or so called critical piping where no residual stresses are to be transferred to the pipe it is a common practice to use CES. In a constant effort support the load remains constant when the pipe moves from its cold position to the hot position. Thus irrespective of travel the load remains constant over the complete range of movement. Therefore it is called a constant load hanger. Compared to a variable load hanger where with movement the load varies & the hot load & cold load are two different values governed by the travel & spring constant. A CES unit does not have any spring rate.
Different Types of Special Pipe Support:
Spring Hangers/Can Type Supports
The use of spring hangers and can type supports is quite common in critical processes and power plant units. Lines operating at high temperature move upwards/downwards (depending on the pipe configuration) due to thermal expansion. Variable spring supports are useful in high temperature, high pressure conditions as they have a spring element that gets compressed or flexed when there is thermal movement of pipe and related loads.
Rigid supports don’t work in such conditions and may cause breakdown.
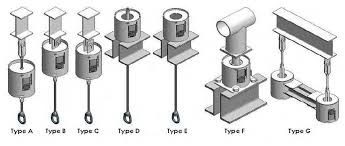
The spring hangers give continuous support when there is expansion or contraction of the pipe.
Application: To minimize piping loads on nozzles, spring supports shall be used.
Rigid/Rod Hangers
Static restraints or rigid support prevent transmission of movement (caused by thermal or vibratory changes) on piping. These rigid supports are vertical type provided from the top and designed to withstand tensile loads. That is no compression load can be exerted over it, otherwise it may cause buckling.
Rigid support consists of clamp, eye nut, tie rod, beam attachment. The selection of rod hanger depends on pipe size, load, temperature, insulation, assembly length etc. The arrangement is quite simple and it is very widely used in piping. As it comes with hinges and clamp, no substantial frictional force comes into play.

Rod hangers offer support in the vertical direction and allows limited motion in the horizontal direction. Adjustment in the vertical direction is achieved by threads or a turnbuckle.
Application: To transfer piping loads on vertical structure where space constraints for provision of pipe supports below, rigid/rod hanger supports shall be used.
Rigid Struts
Rigid Struts are essentially used as compression and tension elements to reduce dynamic load. They can handle both tensile and compression loads – the struts can be provided in both vertical and horizontal direction. The selection depends on pipe size, load, temperature, insulation, assembly length. Rigid struts come with hinge and clamp, so no substantial frictional force comes into play.
Rigid Struts are used in Pump, Turbine and Compressor connected lines near the nozzle connections to take the advantage of very less friction.
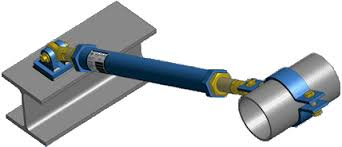

Application:Struts can be used as a substitute for guide supports where structure is not available for using standard guides.
Sway Braces
Sway Braces are shock arrestors, that stop all movement caused by sudden loads in a pipe system. It is used to decrease pipe vibration amplitude, dampen the load and reduce overall movement. It stops the pipes from vibrating at their resonant frequency.

Application: Sway braces are used for restraining vibration, arresting shock, leading, guiding or controlling the pipe movement resulting from thermal expansion.
Hydraulic and Mechanical Snubbers
Snubbers are devices used to restrain pipe and equipment movement during abnormal dynamic conditions like turbine trips, safety/relief valve discharge, earthquakes etc. The snubber design allows free thermal movement of a component during normal operation conditions, but confines the component in abnormal conditions.


Application: Snubbers are used to restrain the movement of pipe and equipment during abnormal dynamic conditions such as earthquakes, turbine trips, safety/relief valve discharge and rapid valve closure.
Sliding Supports
A slide plate is used to produce a low-coefficient of friction between stationary support elements and moving components to decrease the forces/friction that is caused by pipe deflections.
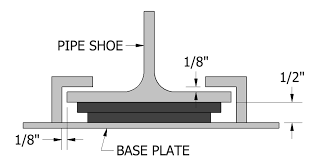
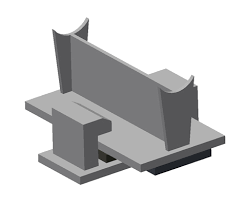
Application: To minimize piping loads on nozzles due to friction, sliding supports shall be used. They are applied variedly to provide piping support, especially in heavy equipment such as pressure vessels, and structural steel members.





































0 Comments: